Overview of Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is the second most common type of dementia.
It results from reduced blood flow to the brain, leading to cognitive impairment.
The condition can develop after a stroke or from other factors that damage blood vessels in the brain.
Causes of Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia is caused by conditions that affect blood flow to the brain. The most common causes include:
- Stroke – A major stroke or multiple small strokes (multi-infarct dementia) can block blood vessels in the brain, leading to brain damage.
- High blood pressure – This condition can weaken or damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of vascular dementia.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the brain.
- High cholesterol – Excess cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup, restricting blood flow.
- Blood vessel disease – Narrowing or damage to blood vessels in the brain reduces oxygen supply, leading to cognitive impairment and dementia.
- Underlying causes – Conditions such as heart disease and lifestyle factors like smoking and obesity also increase the risk of vascular dementia.
Risk Factors for Vascular Dementia
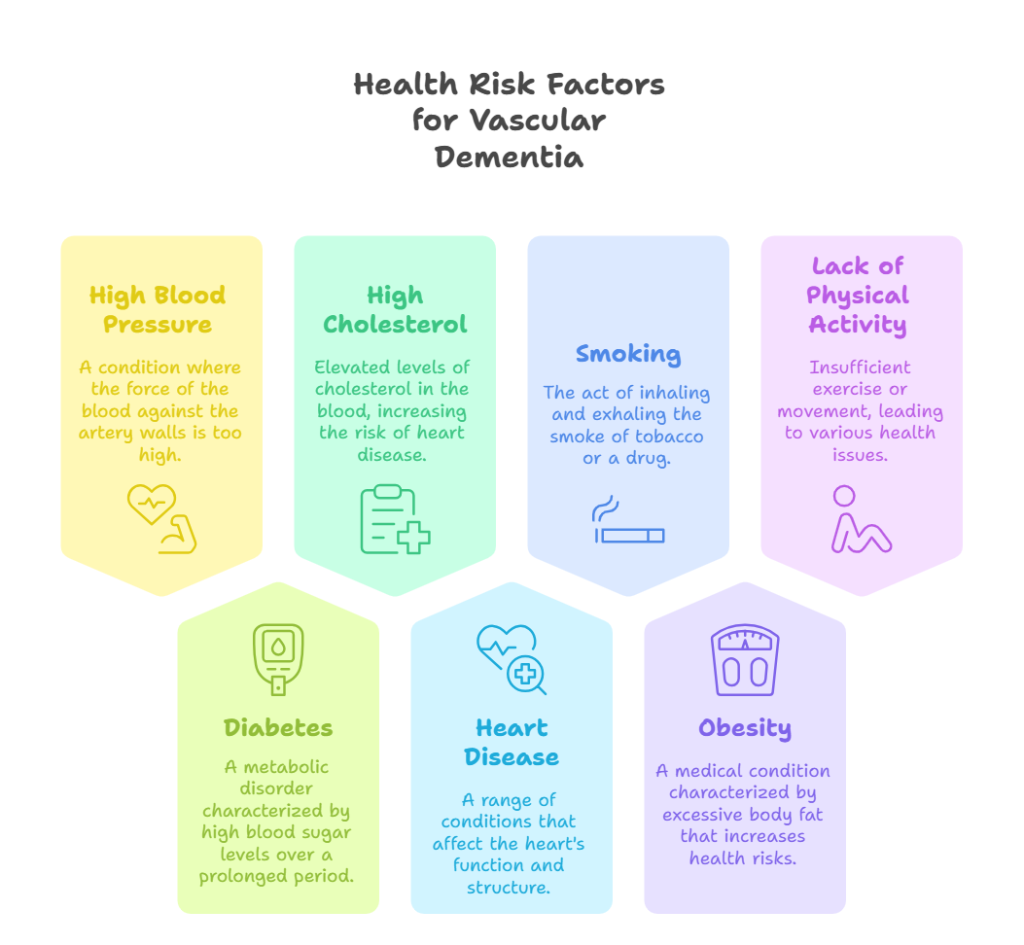
Several risk factors for vascular dementia include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
The biggest risk factor for vascular dementia is age. The risk of vascular dementia increases as people get older.
Symptoms of Vascular Dementia
Vascular dementia symptoms vary depending on the part of the brain affected.
Signs and symptoms of vascular dementia include:
- Problems with memory
- Difficulty with decision-making
- Trouble concentrating
- Slowed thinking
- Mood changes
Symptoms may get worse over time, leading to severe cognitive impairment.
Diagnosis of Vascular Dementia
Doctors diagnose vascular dementia using medical history, cognitive tests, and brain imaging.
The National Institute on Aging provides guidelines for diagnosing vascular dementia.
How to Reduce Your Risk of Vascular Dementia
A healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of dementia, including vascular dementia.
Ways to reduce your risk of vascular dementia include:
- Controlling high blood pressure
- Managing diabetes
- Lowering cholesterol levels
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a balanced diet
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
Treating Vascular Dementia
There is no cure for vascular dementia, but treatment can slow the progression of dementia.
Doctors may prescribe medications to manage high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
A healthy lifestyle can also improve symptoms.
Final Thoughts
Vascular dementia is a common type of dementia caused by reduced blood flow to the brain.
Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke.
People with vascular dementia also have an increased risk of developing other forms of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Early diagnosis and a healthy lifestyle can help slow the progression of dementia and improve quality of life.




